Time Of Flight Proton RADiography
with plastic scintillators
| The TOFpRad project aims at studying the feasibility of a plastic scintillator-based Time of Flight (TOF) proton radiography system to support the planning and the verification of charge particle treatments. |
| Ion beam therapy represents the preferable solution in the treatment of many radiation-resistant and deep-seated tumors, given the capability to deliver high amounts of dose in depth around the Bragg Peak and given the high radiation biological effectiveness of heavier ions. However, large dose gradients impose a thorough planning and verification of the treatment to ensure the correct irradiation of the tumor volume and the sparing of the healthy tissues. Current limitations in the available technology hinder the full exploitation of the potential of this technique, imposing large safety margins and giving only a limited supervision during the irradiation sessions, thus mining the efficacy of the therapy. |
| Proton transmission imaging has the potential to tackle these limitations by enhancing the accuracy of the treatment planning, correcting the mismatch between the stopping power of the tissues, i.e. describing the slowing down of ions, and the attenuation coefficients, i.e. describing the attenuation of X-rays, estimated by means of a computed tomography scan. Moreover, proton transmission imaging can be also employed as a verification tool to monitor and validate the irradiation scheme before each session. |
| Several proton imaging prototypes have been investigated in the last 15 years. All of these rely on calorimeter detectors to measure the protons’ residual energy. Energy detection via TOF, on the other hand, has hardly been explored in proton imaging so far although the method is well-established in other fields such as particle physics. |
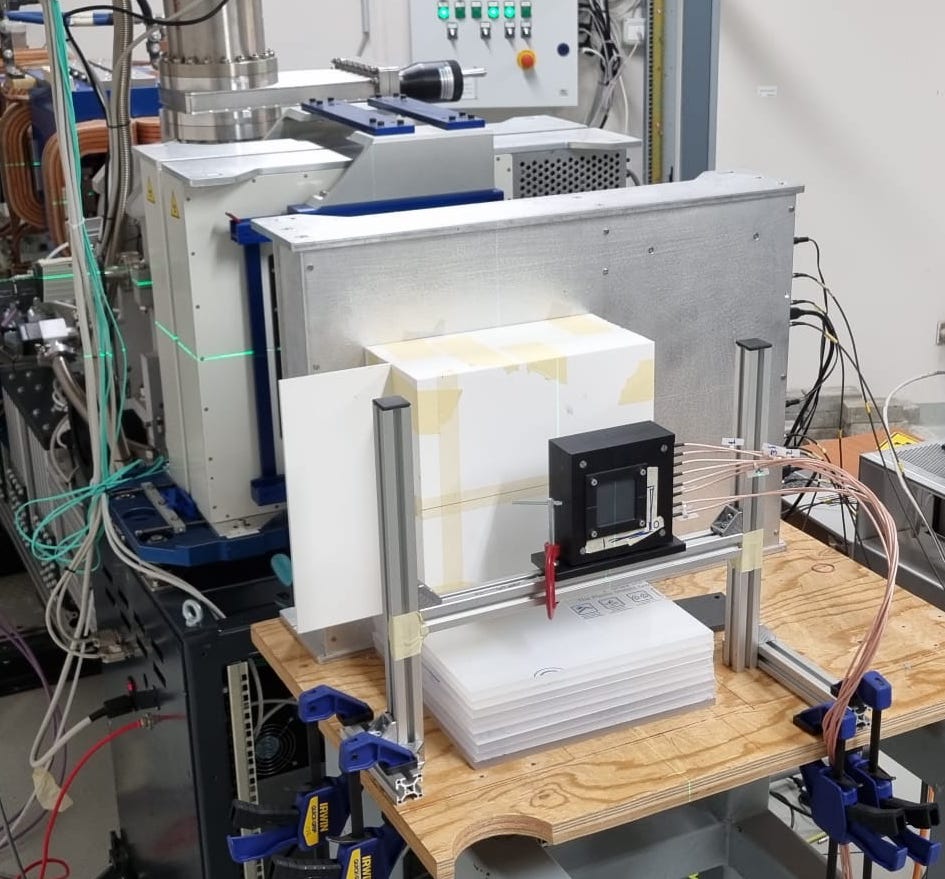
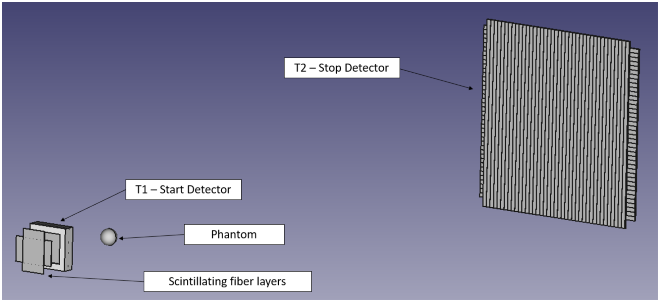
| The TOFpRad project will develop a proton radiography demonstrator featuring a TOF system and plastic scintillator fibers that track the position, the direction and the residual energy of high energy protons. The TOF system will be composed of two plastic scintillator detectors read-out by Silicon Photomultipliers. The apparatus will be tested at the Centro Nazionale di Adroterapia Oncologica (CNAO) using proton beams on dedicated phantoms. The project will demonstrate the groundbreaking benefits that a clinical system based on the TOFpRad technology will introduce in the particle therapy scenario. |