| The external beam radiotherapy research community is currently experiencing an exciting time: experimental evidence is growing, supporting the evidence of a considerable normal tissue sparing effect when treatments are delivered with dose rates much larger (100 times or more) with respect to the conventional ones. If confirmed, this so-called ‘FLASH effect’ has the potential to re-shape the future of radiation treatments especially with charged particles, with a significant impact on many oncology patients. |
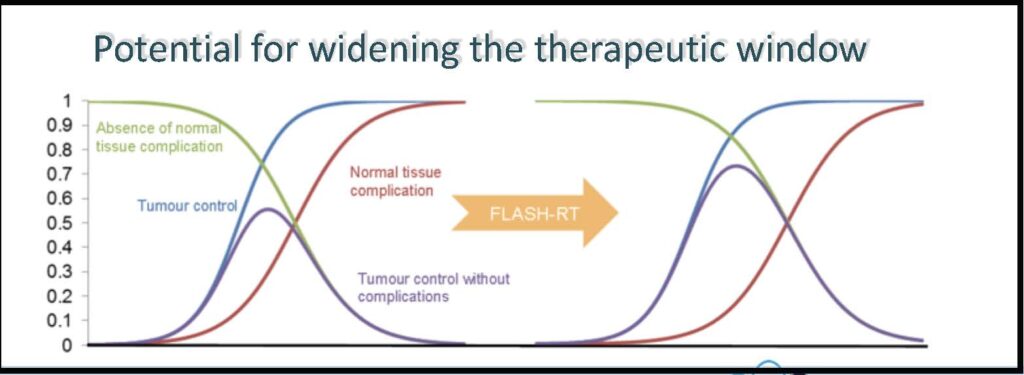
| FLASH Radiotherapy, is a novel approach of radiotherapy using ultra-high dose rate (>40 Gy/s overall dose rate, for a total irradiation time <100 ms , but much higher rates (up to 109 Gy/s) during each pulse) aiming to get unchanged tumor control and protection in the normal tissue. |
| The FRIDA (Flash Radiotherapy with hIgh Dose-rate particle beAms) project addresses several challenges posed by this potential revolution. A crucial task is represented by the mechanistic understanding and modeling of the effect. Another key ingredient is the necessary research and development phase in the acceleration and beam delivery fields to provide the required dose rates with a clinically acceptable precision. A final word on the FLASH effect will be said only if novel beam monitoring and dosimetry techniques capable of sustaining very high dose rates will be developed. Finally, software tools for FLASH treatments planning are needed to evaluate the technique potential and enable clinical applications. |
| Within INFN and CSN5 activities, the know-how and expertises needed to make a step forward in this field are presently available. Experiments are carried out at FLASH beam facilities that are (or will be in the near future) available, complementing the multiscale FLASH mechanism modeling efforts. LINAC and laser-plasma techniques will be applied to the delivery of FLASH e– and p beams. Detection and monitoring techniques are developed and tested, as well as the implementation of software tools needed for the simulation and treatment optimization tasks. |